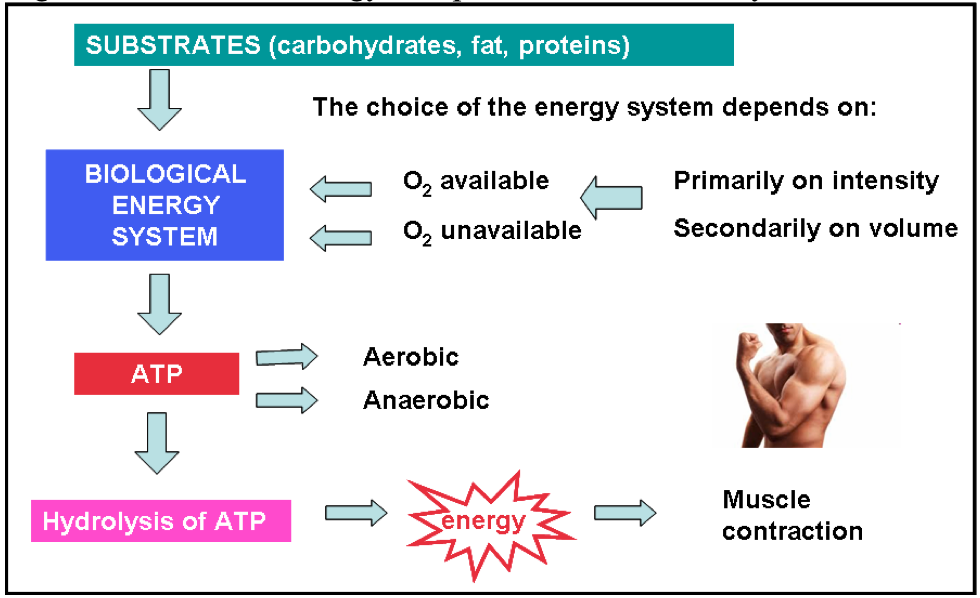
What Is the Primary Substrate to Provide Energy at Rest
Carbohydrates are used when the body is at rest it also depends on fat. The oxidative system the primary source of ATP at rest and during low-intensity activities uses primarily carbohydrates and fats as substrates.

1 Substrate Utilization During Resting State
-Energy yield 1 mol ATP per 1 mol PCr 2.

. The total amount of CP and ATP stored in muscles is small so there is limited energy available for muscular contraction. PCrs role in energy production is to regenerate ATP to maintain a relatively constant supply under resting conditions and recycle ATP during exercise until its used up. What is the primary substrate used to provide energy at rest during high intensity exercise.
During high intensity exercise more carbohydrates are used than any other substrate. During short-term intense activities a large amount of power needs to be produced by the muscles creating a high demand for ATP. Oxidative System oxidative phosphorylation-Aerobic-Glycolysis Krebs cycle ETC.
During aerobic work 50-60 of the energy comes from fats Primarily carbohydrates are used during the first several minutes of exercise. Fuel sources from which we make energy ATP carbohydrate fat protein. Pyruvic acid converted to lactic acid when no O2-Energy yield 1 mol glucose yields 2 mol ATP.
Fats and carbs are the primary substrates that are used. The oxidative energy system is the primary source of ATP at rest and during low intensity exercise. The process by which fatty acids and other sources are converted to energy during low.
The energy used in post-prandial state during rest and physical activity is derived predominantly from the oxidation of carbohydrate CHO and fat. Muscle carbohydrate stores glycogen blood sugar blood fatty acids and intramuscular triacylglycerols. Solution for What is the primary substrate used to provide energy at rest.
-Energy yield 1 mol ATP per 1 mol PCr 2. Want to see the full answer. This system uses creatine phosphate CP and has a very rapid rate of ATP production.
Pyruvic acid converted to lactic acid when no O2-Energy yield 1 mol glucose yields 2 mol ATP. 2What is the primary substrate used to provide energy at rest. 1 mol glycogen yields 3 ATP 3.
66 comes from fat. Fats and carbs are the primary substrates that are used. Energy is stored in the body in various forms of carbohydrates fats and proteins as well as in the molecule creatine phosphate.
The other energy systems ATP-PC and Glycolysis provide energy for shorter duration and higher. Although protein can also serve as a source of energy amino acids oxidation is usually tightly adjusted to amino acids intake and their contribution to total energy expenditure is rather. The oxidative energy system is the primary source of ATP at rest and during low intensity exercise.
After about 90 seconds of continuous physical exertion this energy system will kick in. Glycolytic System glycolysis-Anaerobic-Glucoseglycogen broken down to pyruvic acid. 1 mol glycogen yields 3 ATP 3.
Pyruvic acid converted to lactic acid when no O2-Energy yield 1 mol glucose yields 2 mol ATP. Adenosine triphosphate high-energy compound 2. The measurement of substrate utilization patterns is commonly used to evaluate functional diversity of bacterial populations.
Glycolytic System glycolysis-Anaerobic-Glucoseglycogen broken down to pyruvic acid. At rest and during normal activities fats contribute 8090 of our energy. -Energy yield 1 mol ATP per 1 mol PCr 2.
- ATP is a high energy compound in the body the usable storage form of energy derived from food. First week only 499. Carbohydrate and fat are the primary sources of energy with protein contributing a minimal amount under normal conditions.
The commercially available Biolog system which contains 95 carbon and energy sources on one microtiter plate is widely used because of its convenience. The phosphagen system also called the ATP-CP system is the quickest way to. Glycolytic System glycolysis-Anaerobic-Glucoseglycogen broken down to pyruvic acid.
- It is used during as fuel. Performed at cellular level. Carbohydrates provide 518 and protein 25.
Start your trial now. Oxidative System oxidative phosphorylation-Aerobic-Glycolysis Krebs cycle ETC. Check out a sample QA here.
The creatine phosphate is used to reconstitute ATP after its broken down to release its energy. The other energy systems ATP-PC and Glycolysis provide energy for. PCrphosphocreatine or creatine phosphate.
While at rest and during low-intensity exercise free fatty acids are the predominant energy sources. 1 mol glycogen yields 3 ATP 3. At rest carbohydrates and fats are almost equally used as the primary substrates for energy.
Process of converting substrates into energy. The primary substrates or carbohydrates 50 and fats 50 provide energy at rest. Oxidative System oxidative phosphorylation-Aerobic-Glycolysis Krebs cycle ETC.
Carbohydrates provide energy for high-intensity exercise. During exercise there are four major endogenous sources of energy. The extent to which these substrates contribute energy for.
Following the onset of activity as the intensity of exercise increases there is a shift in substrate preference from fats to carbohydrates. Fat is your bodys preferred source of energy for low-intensity exercise. Although protein can also serve as a source of energy amino acids oxidation is usually tightly adjusted to amino acids intake and their contribution to total energy expenditure is rather insignificant in healthy subjects.
At rest 33 of the bodys energy comes from carbohydrates or glycogen stored within the muscles and liver. The energy used in post-prandial state during rest and physical activity is derived predominantly from the oxidation of carbohydrate CHO and fat. Adenosine triphospate ATP is the bodys usable form of energy.

1 Substrate Utilization During Resting State

Energy Substrates For Exercise The Source Of Energy Substrates During Download Scientific Diagram

No comments for "What Is the Primary Substrate to Provide Energy at Rest"
Post a Comment